Our team is happy to announce a new version of the Aleo Stack, which includes the node implementation snarkOS and the programming language Leo. These applications are built on top of the developer-friendly snarkVM and Aleo SDK libraries. Aleo is an open source cryptocurrency through which developers can deploy cryptographically secure dApps.
Most notably, this release unlocks a reduction of base fees by 90%, as well as the introduction of priority fees. This effectively creates a fee market, allowing users to bid in order to get a higher priority in the mempool. The release also introduces various quality of life improvements such as new /v2/ snarkOS endpoints with more informative responses, performance improvements, as well as a `Leo update` command.
If you want to try it out, you can build from source today or download the mainnet release from github September 9th. Find the current release schedule at: https://provablehq.github.io/.
Please report any issues you might come across!
What's new in snarkOS v4.2.0
Consensus change: ConsensusVersion V10
A consensus change will occur at the following times:
Canary - ~9AM PT August 29th, 2025
Testnet - ~9AM PT September 5th, 2025
Mainnet - ~9AM PT September 16th, 2025
The exact block heights will be encoded in the snarkVM library at release.
ATTENTION: Validators that do not upgrade in time will be at risk of forking and require manual intervention. Clients that do not upgrade will be at risk of halting until an upgrade occurs.
Reduced Fees + Priority Fees
The use of zero knowledge cryptography in Aleo enables a highly scalable blockchain network. However, those scalability benefits have not translated into low fees on the Aleo network - yet. Because of a large focus on security, high fees have served as an additional layer of defense against Denial of Service attacks. The time has come to deliver on the promise of zero-knowledge proofs, and to make transactions cheap.
Technically, this will soon be possible because of the spend limits which are introduced, acting as another layer of defense against high compute. As such, this ARC proposes to reduce compute-related costs by a factor of 25x, which will significantly bring down average transaction costs by up to 92%. Note that private transfers are not impacted, because they did not incur any compute costs, which was the aspect which has been discounted.
Example deployment cost reduction
Program | Price before [microcredits] | Price after [microcredits] | Reduction [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
credits.aleo | 134,619,400 | 115,123,243 | 14.4 |
grant_disbursement_arcane.aleo | 13,805,525 | 8,953,181 | 35.1 |
Example execution cost reduction
Function | Price before [microcredits] | Price after [microcredits] | Reduction [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
credits.aleo transfer_public execution | 34,060 | 2,725 | 91.9 |
credits.aleo transfer_private execution | 2,242 | 2,242 | 0 |
Priority fees
This release also introduces priority fees which effectively create a fee market, allowing users to bid in order to get a higher priority in the mempool.
In more technical detail, this PR introduces a priority queue for transactions containing a nonzero priority fee. This is drained before the pre-existing transactions queue when sending transactions to the BFT.
A few notes on the current design:
Priority fees for transactions already in the mempool cannot be updated.
There is no protection against starvation: if the priority pool stays full enough, transmissions from the standard queue will not be sent to the BFT.
Batch building is not atomic w.r.t. the memory pool.
New endpoints
Check transaction on broadcast
Submitting transactions to blockchains and developing on them can be difficult. In order to verify transactions, you need the latest state, and it is ultimately up to consensus to include a transaction into a block, which is a multi-stage opaque process. To improve the quality of life for users and developers, this PR introduces a new feature for nodes allowing them to perform an early optional check on the transaction, and to return the result synchronously to the user:
// POST /<network>/transaction/broadcast?check_transaction={true}The reason this is optional, is that for many applications, performance is critical, so the default behaviour is the same as before: the user gets a response just confirming receival, not approval.
Fetching a batch of statePaths
This PR adds a new REST endpoint that allows users to fetch multiple state paths at once. This will help mitigate the global state root to be the same across iterations issues seen when users/provers are querying for state.
GET /<network>/statePaths?commitments=cm1,cm2,...The commitments in the query string are comma separated. At most 16 commitments can be fetched at a time.
Informative snarkOS JSON-RPC responses
snarkOS now supports versioned API endpoints. This change is backwards compatible, meaning by not indicating any version, or by using the /v1/ prefix, the original responses will be used.
New /v2/ snarkOS endpoints have been introduced which return more informative error messages. Instead of only returning a 500 or 429, the REST API now returns the error chain as JSON It will (try to) set the HTTP status code correctly:
/// 400 Bad Request - Invalid input, malformed parameters, validation errors
/// 404 Not Found - Resource not found
/// 422 Unprocessable Entity - Business logic validation errors
/// 429 Too Many Requests - Rate limiting
/// 503 Service Unavailable - Temporary service issues (node syncing, feature unavailable)
/// 500 Internal Server Error - Actual server errors, unexpected failures
These new return codes may become available via updated explorer APIs as well.
Improvements for node operators
Some further improvements worth mentioning include:
Networking code has been significantly cleaned up, leading to fewer spurious connection issues. (#3754)
Syncing has been further sped up and stabilized (#2745)
Running a network with the `test_network` feature now prints more low level debugging information.
Peers can now be specified both by IPs and hostnames. (#3768)
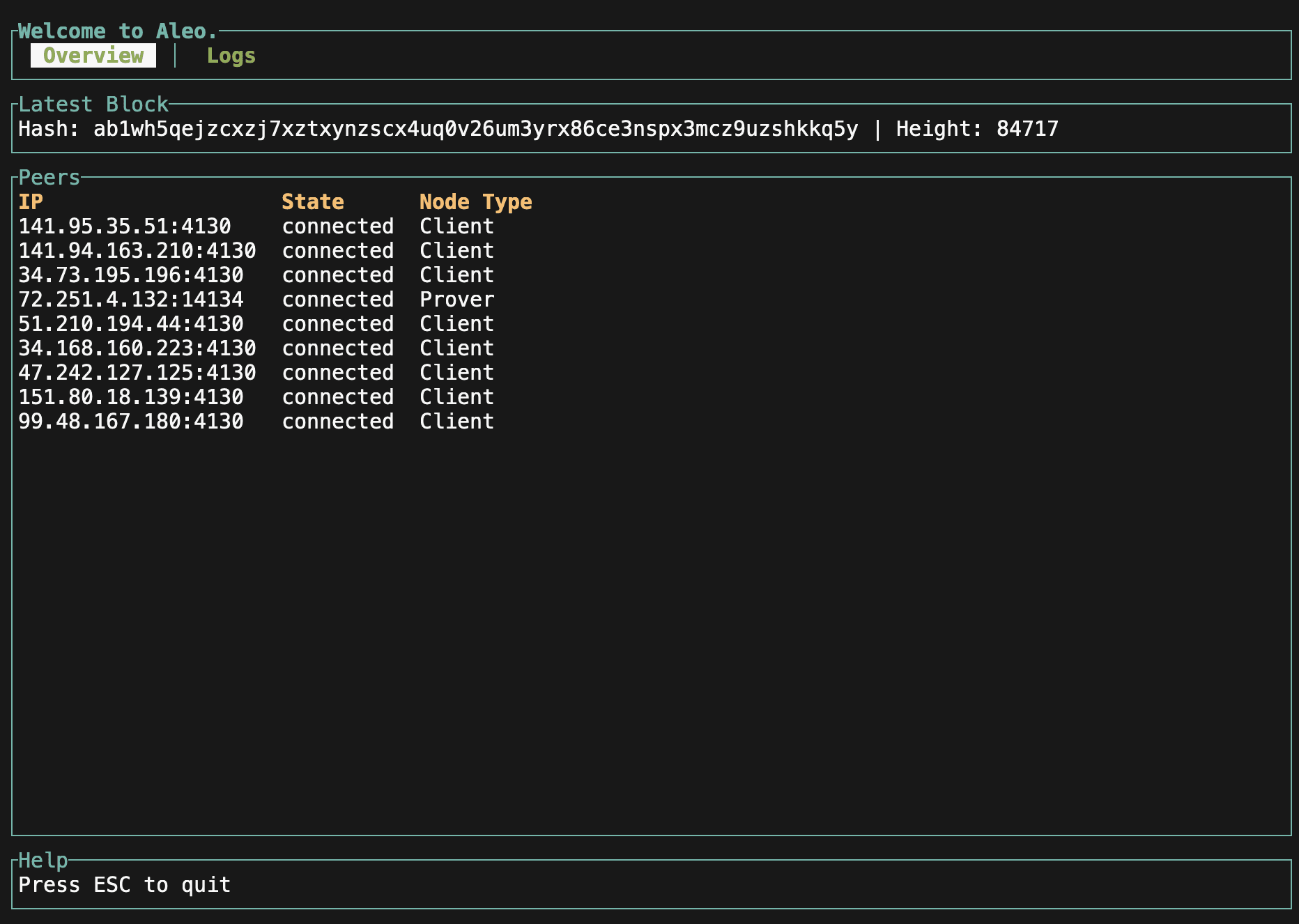
./snarkos start --peers "validator0:4130,client0:4130"The "Overview" page in the terminal UI (display) is usable again. It now shows the currently connected peers and information about the latest block. (#3767)
What’s new in Leo 3.2.0
Leo Modules
Leo 3.2.0 comes with a module system.
Given a file other_module.leo containing struct, const, and inline definitions like this:
const X: u32 = 2u32;
struct S {
a: field
}
inline increment(x: field) -> field {
return 1field;
{You may refer to contents of the module as other_module::X, other_module::S, and other_module::increment.
📁 Example Directory Structure
src
├── common.leo
├── main.leo
├── outer.leo
├── outer
│ ├── inner.leo📦 Module Access Paths
Given the structure above, the following modules are defined:
common.leodefines modulecommon, accessible frommain.leovia:common::<item>outer.leodefines moduleouter, accessible frommain.leovia:outer::<item>outer/inner.leodefines submoduleouter::inner, accessible from:main.leo:outer::inner::<item>outer.leo:inner::<item>
📏 Module Layout Rules
This PR also enforces new rules to prevent ambiguity and ensure consistency:
Leaf modules (i.e. modules without submodules) must be defined in a single file:
foo.leoModules with submodules must be defined by an optional top-level
foo.leofile and afoo/directory containing the submodules:
foo.leo # defines module `foo` - this is optional
foo/
├── bar.leo # defines submodule `foo::bar`Only relative paths are implemented so far. That means that items in outer.leo cannot be accessed from items in inner.leo, for example. This is limiting for now but will no longer be an issue when we add absolute paths.
Leo Update
leo update now allows you to select a particular version to install:
leo update --name v3.0.0Remaining stability improvements
leonow allows you to decrypt records via the CLI. You may also pass in record ciphertexts as inputs toleo executedirectly.Bug fix in outputting code regarding parenthesizing operands of the ternary conditional.
Bug fix: eliminate redundant type errors in async function calls.
Bug fix: correctly handle shorthand struct initializers which are consts.
Bug fix:
leo cleandoesn’t produce errors when outputs or build directory isn’t present.Bug fix: correctly type check
returnstatement in a constructor.Bug fix: check
snarkosinstallation location.Bug fix: const evaluate const args before monomorphizing.
Improved error messages for unresolved generics.
Library and tooling updates
What’s new in SDK v0.10.0
Updates to the KeyProvider interface with methods that enable local storage + implementations of the KeyProvider interface that store Proving and Verifying keys in local storage in Node.js and browser storage in browser contexts. This allows function executions to use locally stored keys to speed up execution.
Update to the RecordProvider interface to enable metadata to be included with found records + implementations of the RecordProvider interface that allow users of the SDK to efficiently search for their own records.
ProgramManager methods now accept object parameters instead of individual parameters. This enables developers to supply only required parameters to ProgramManager functions. Developers upgrading to v1.0.0 will need to make slight changes to their invocations of ProgramManager methods.
Fixes that allow private transactions involving records to succeed consistently via a custom implementation of the QueryTrait.
snarkVM v4.2.0
snarkVM is a zkVM library. It powers the Aleo network and most of the software used to interact with it. The following contains some of the most relevant changes which were introduced:
fn deployment_costwas renamed tofn deployment_cost_v1fn deployment_costandfn execution_costwere introduced to allow for switching on the cost function based on ConsensusVersionfn find_recordsnow filters records by ownership before decryption in #2691This PR implements
get_state_paths_for_commitmentsto retrieve a batch of state paths rather than one at a time in the query. This will help mitigate the global state root to be the same across iterations issues seen when users/provers are querying for state.A floating‑point sqrt and type conversion was replaced by isqrt to support WASM-based platforms which don’t support floating point operations, in #2835
Support building snarkVM on SGX in #2791, enabled by the introduction of a
filesystemfeature, without which, the parameters crate won’t require a filesystem anymore to store parameters.fn authorize_requestwas introduced, which allows offline hardware wallets to sign a Request without importing the entire VM object. This is possible only for individual functions with public inputs and outputs, such ascredits.aleo::transfer_public.The total amount of TestRNG call counts are now printed at the end of test runs to help facilitate debugging.
This PR changes the Query type to use http::Uri internally for enhanced debugging.
Closing notes
The full changelogs for the referenced releases can be found here:
https://github.com/ProvableHQ/snarkVM/compare/v4.1.0...testnet-v4.2.0
https://github.com/ProvableHQ/snarkOS/compare/v4.1.0...testnet-v4.2.0
If you want to try it out, you can build from source today or download the mainnet release from github September 9th. Find the current release schedule at: https://provablehq.github.io/.
Contributors
A big thank you to all the contributors on Github to this snarkOS, Leo, SDK and snarkVM release!
@acoglio
@anstylian
@antonio95
@christianwwwwwwww
@damons
@d0cd
@kaimast
@iamalwaysuncomfortable
@ljedrz
@meddle0x53
@mohammadfawaz
@mikebenfield
@niklaslong
@raychu86
@rejected-l
@Roee-87
@trevor-crypto
@vicsn
